Early Signs of Cavities in Children
Cavities can develop quickly in growing smiles, and the earliest warning signs are often subtle. Knowing what to watch for helps parents act before decay progresses and requires more involved treatment. Understanding the early signs of cavities in children empowers families to prevent problems before they start. Use this guide to spot early signs of cavities in children, understand what causes them, and learn practical steps to keep your child’s teeth healthy.
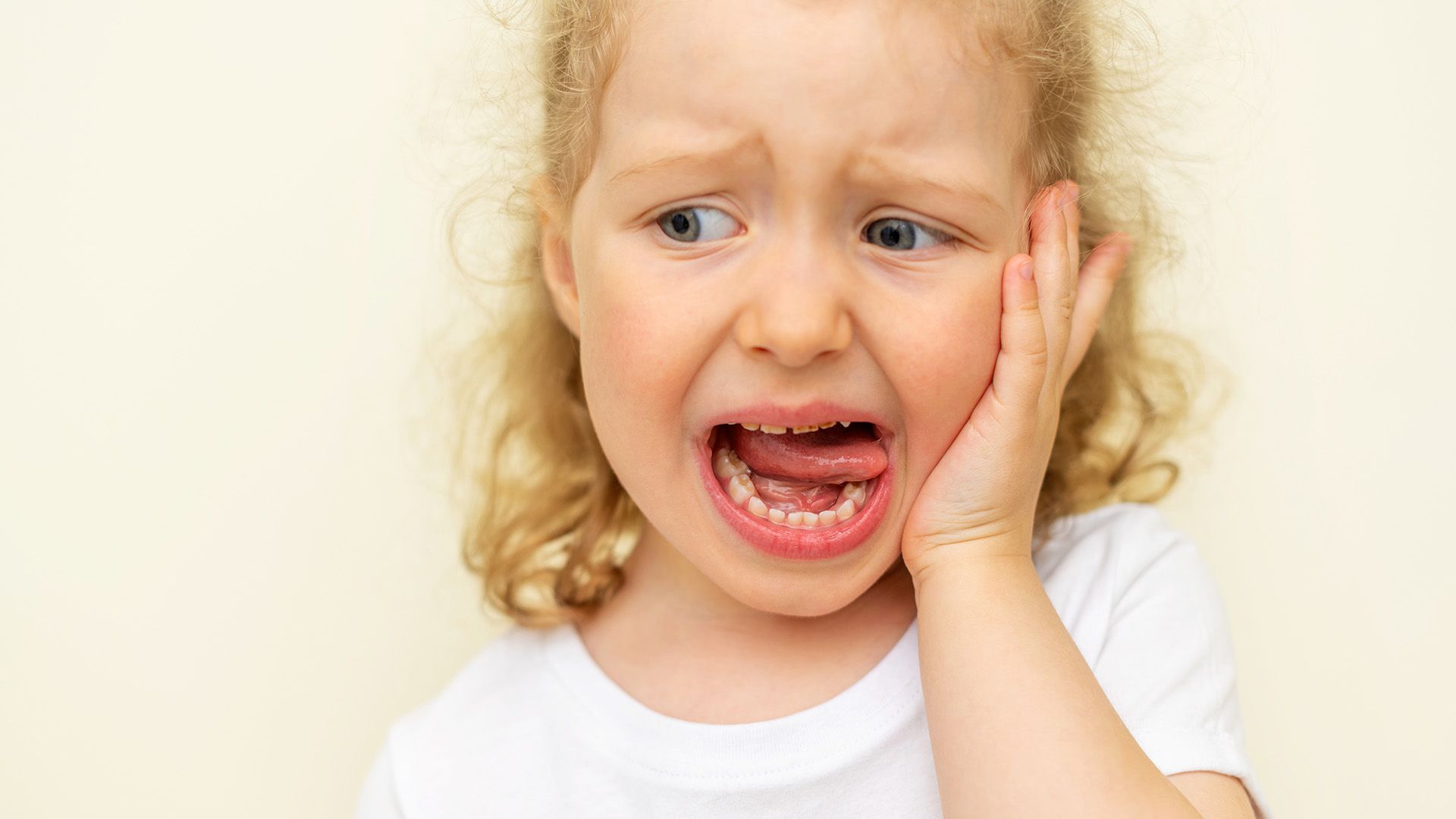

Understanding Tooth Decay in Children
Tooth decay occurs when bacteria in the mouth feed on sugars and produce acids that weaken tooth enamel. Over time, this softening of the enamel can cause permanent damage, forming cavities that may spread deeper into the tooth. In the earliest stage, early tooth decay often appears as matte or chalky white spots caused by demineralization; as it advances, these areas can turn brown or black and eventually develop into small holes.
Baby teeth (primary teeth) have thinner enamel than permanent teeth, which makes them more vulnerable to rapid decay. Because primary teeth guide the eruption and alignment of adult teeth, keeping them healthy supports proper spacing and bite development, critical factors during orthodontic treatment. Preventing pediatric tooth decay in these early years helps set the stage for long-term oral health.
Early detection matters because small problems are easier and less invasive to treat. When parents and caregivers recognize changes quickly, dental teams can strengthen weak enamel, apply protective treatments, and offer guidance to prevent further damage. Prompt attention to early tooth decay helps preserve comfort, chewing function, and confidence in your child’s smile.
Recognizing the Early Signs of Cavities
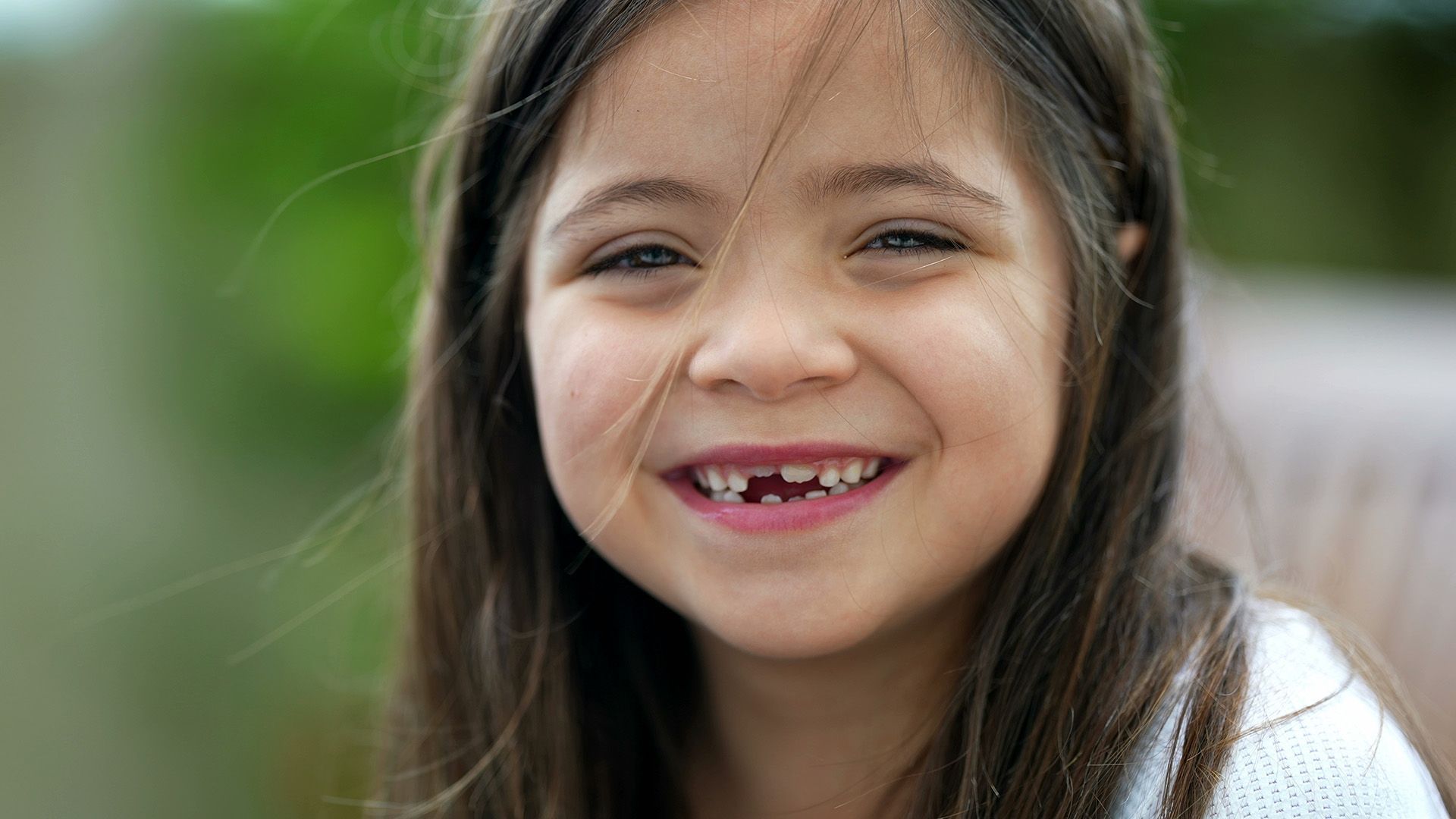
Visual clues often appear before pain. Inspect your child’s teeth in good lighting, especially along the gumline and between teeth where decay commonly starts. Early lesions may look like chalky white spots or dull, opaque areas on the enamel; as decay progresses, tiny pits or holes can form. These are among the early signs of cavities in children that are easiest to see at home.
Changes in tooth color or texture can include:
- White, opaque patches indicating weakened enamel
- Yellowing near the gumline from plaque buildup
- Brown or black specks that do not brush off
- Rough or uneven edges where enamel has eroded
These changes may be easier to spot on front teeth but frequently occur on molars.
Behavioral signs can be subtle. Children might complain about sensitivity to cold water, hot foods, or sweet snacks. They may avoid chewing on one side, feel mild discomfort while brushing, or report a lingering bad taste. Persistent bad breath and irritation of the gums near a tooth can also accompany early decay. If your child is wearing orthodontic appliances, pay close attention to areas around brackets and wires where plaque can accumulate, these areas are common sites for pediatric tooth decay to begin.
Factors Contributing to Tooth Decay
Diet plays a major role in cavity risk. Frequent snacking on sugary foods, sticky treats, and sweetened drinks creates a continuous acid attack on enamel. Even seemingly healthy choices like dried fruit or sports drinks can be high in sugars. Sipping juice or sodas over a long period is more harmful than consuming them with meals because teeth are exposed to sugar more often, increasing the likelihood of early tooth decay.
Poor oral hygiene allows plaque, a biofilm of bacteria, to remain on teeth. Incomplete brushing, skipping flossing, and inadequate cleaning around orthodontic brackets increase the likelihood of decay, particularly in hard-to-reach areas. Night-time habits such as going to bed without brushing or drinking sugary beverages elevate risk because saliva flow decreases during sleep, which can accelerate pediatric tooth decay.
Some children may be more prone to cavities due to genetics and environmental factors. Thinner enamel, deep grooves in teeth, or reduced saliva flow can increase susceptibility. Limited exposure to fluoride, mouth breathing, and certain medications can also affect the mouth’s natural defenses. Recognizing these contributors helps tailor prevention strategies for your child’s needs and makes it easier to identify the early signs of cavities in children.
Preventive Measures for Healthy Teeth
Establish a consistent dental care routine early. Brush twice daily with a fluoride toothpaste, floss every day, and take extra care cleaning around orthodontic appliances. Supervise brushing until your child demonstrates proper technique, and use a soft-bristle brush or orthodontic brush to reach around brackets and wires. Encourage water between meals and after snacks to help rinse away acids and reduce the risk of early tooth decay.
Fluoride strengthens enamel and can help reverse early demineralization. Ask your dental provider about fluoride varnish applications and the appropriate toothpaste strength for your child’s age. Dental sealants offer an additional layer of protection by covering deep grooves on molars where food and bacteria can hide. These preventive treatments are especially helpful for children with higher cavity risk or early signs of pediatric tooth decay.
Routine dental checkups allow professionals to identify early changes and intervene promptly. Regular visits complement orthodontic care by ensuring teeth and gums stay healthy while alignment progresses. If you notice white spots, sensitivity, or any color changes, schedule an evaluation. Coordinated care with your child’s dentist supports comprehensive oral health during treatment and provides guidance on effective home care to help prevent pediatric tooth decay.
When to Contact a Dental Professional
Schedule an appointment if you see persistent white spots, dark stains that do not brush away, sensitivity to sweets or temperatures, or any visible pits on the teeth. Early intervention may include remineralization treatments, sealants, or small fillings that stop decay before it spreads. For children in braces or other appliances, timely care prevents complications that can impact treatment progress and helps halt early tooth decay.
If concerns arise between regular visits, reach out, early support can make a meaningful difference in your child’s comfort and long-term dental health. Being proactive when you notice the early signs of cavities in children leads to simpler, more successful treatment.
Support for Long-Term Oral Health
Healthy teeth are essential for successful orthodontic outcomes. Families and dental professionals can work together to reduce cavity risk, provide appliance-specific hygiene guidance, and identify early signs of problems. From tailored brushing techniques to product recommendations, the goal is to keep your child’s smile strong throughout treatment and minimize pediatric tooth decay.
Learn more about preventing cavities, recognizing the earliest signs of decay, and protecting your child’s smile during orthodontic care. With consistent habits and timely checkups, you can address early tooth decay effectively and support lifelong oral health.